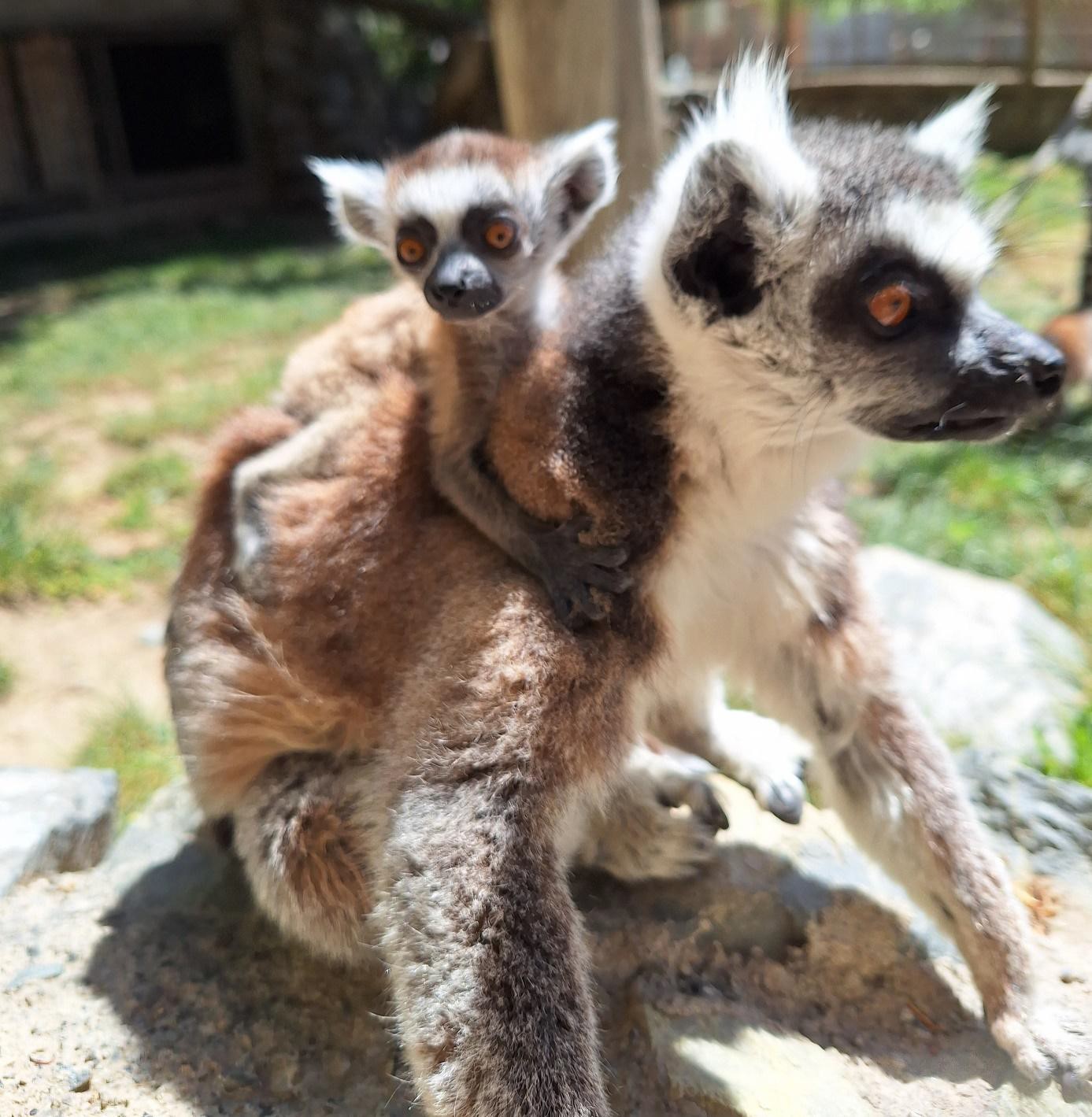
Toxoplasmosis in the herd of ring-tailed lemurs (Lemur catta) under human care and its medical management
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.19137/cienvet202426206Keywords:
Lemur, Toxoplasmosis, Abortion, HatchlingAbstract
This work aims to offer information about the diagnosis and the medical management of toxoplasma gondii infection in a ring-tailed lemur mix squad composed of 5 individuals (3 males and 2 females) under human care in a zoo collection of the 6th region of Chile. The 8-year-old female was presented with fever, lethargy, appetite loss, and abortion of a newborn at term. A clinical exam was performed, and hematologic and biochemistry tests, in addition to serology of infectious diseases under anesthesia to the mother and histopathology on the hatchling. The results show Toxoplasma gondii central nervous infection on the hatchling with no other scientific evidence. Cited in the literature, there is some evidence that lemurs are one of the most susceptible species to toxoplasma infection, and sometimes the diagnosis is challenging, after 6 years with no newborns, and after 4 months of treatment, a healthy hatchling was born.
Downloads
References
Salles C J, Mainez M. Localized toxoplasmosis in a ring-tailed lemur (Lemur catta) causing placentitis, stillbirths, and disseminated fetal infection. Sage Journals. Volumen 23, Issue 5. https://doi.org/10.1177/104063871141. 2011
Rocchigiani G, Fonti N, Nardoni S. Toxoplasmosis in captive ring-tailed lemurs (Lemur catta). MDPI. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11101142. 2022
Spencer JA, Joiner KS, Hilton CD. Diseminated toxoplasmosis in a captive Ring-tailed Lemur (Lemur catta). Journal Parasitologist 90 (4), 2004, pp 904- 906. American Society of Parasitologists.

Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Gonzalo Godoy Steindl, M Jimenez

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Al momento de enviar sus contribuciones, los colaboradores deberán declarar , de manera fehaciente, que poseen el permiso del archivo o repositorio donde se obtuvieron los documentos que se anexan al trabajo, cualquiera sea su formato (manuscritos inéditos, imágenes, archivos audiovisuales, etc.), permiso que los autoriza a publicarlos y reproducirlos, liberando a la revista y sus editores de toda responsabilidad o reclamo de terceros , los autores deben adherir a la licencia Creative Commons denominada “Atribución - No Comercial CC BY-NC-SA”, mediante la cual el autor permite copiar, reproducir, distribuir, comunicar públicamente la obra y generar obras derivadas, siempre y cuando se cite y reconozca al autor original. No se permite, sin embargo, utilizar la obra con fines comerciales.





4.png)


7.png)



